EORTC Bladder Cancer Recurrence and Progression Calculator allows you to find the possibility of recurrence and progression of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) over one and five years. So, it considers six parameters related to the patient’s anamnesis and helps you choose the appropriate treatment options.
Our tool will help you find information you search and results easier and simpler, so make sure to continue reading. Also, through this post you will learn more about the bladder cancer symptoms, causes, survival rates and prognosis. In addition, we recommend you to search other related posts on our site, such as Absolute Lymphocyte Count, Flange Size, or Aortic Valve Area.
What Causes Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer is the most common malignancy of the urinary tract. The most common cause of cancer is that it affects people over the age of 60 and more men than women. For instance, smoking is the biggest risk factor, chemicals, chronic infections, previous hand analysis, and family history.
Further, the most typical symptom is painless hematuria or blood in the urine. Don’t forget that! Also, if hematuria is found, always look for bladder or kidney cancer. In addition, this information gives us a closer look at the state of the organism.
At the time of diagnosis, the research has shown that about 75% of patients have NMIBC, while the remaining 25% already have advanced disease. Patients with NMIBC generally have a good survival rate. However, the condition has significant potential for recurrence of bag tumours, which can even progress to a more advanced step of the disease.
Stage 3 and Stage 4
Moreover, there are several stages of this condition. The third and fourth are the hardest. In short, stage 3 of cancer penetrates connective tissue and muscles into the immediate tissue outside the bladder and/or affects the prostate gland in men or the uterus and/or vagina. However, there is no spread to the lymph nodes or beyond in grade III.
On the other hand, stage 4 means that cancer has spread to the wall of the abdomen or pelvis, lymph nodes, or other parts of the body. If it spreads to another part of the body, it will likely go to the bones, lungs, or liver. Further, predictions show that there is a risk of spreading throughout the whole body.
Above all, about 90% of people with cancer are over 55 years old. So, this is the most common risk group. Likewise, the average age of people diagnosed with cancer is 73 years.
Survival rates of cancer by level:
- 5 years: 77 %
- 10 years: 70 %
- 15 years: 65 %
Bladder Cancer Recurrence and Progression: Six Factors
So, the treatment of patients with this cancer should be based on prognosis, which includes the prognosis of recurrence and tumour progression. This EORTC calculator is a tool that predicts the likelihood of recurrence and progression and thus suggests appropriate analysis for patients.
Moreover, this tool is made according to the recommendations of the European Association of Urologists. Also, analysis and research of nearly 2,600 patients first described this process by Sylvester et al. in an article entitled Predicting Recurrence and Progression in Individual Patients with Level Ta T1 Bladder Cancer Using EORTC Risk Tables.
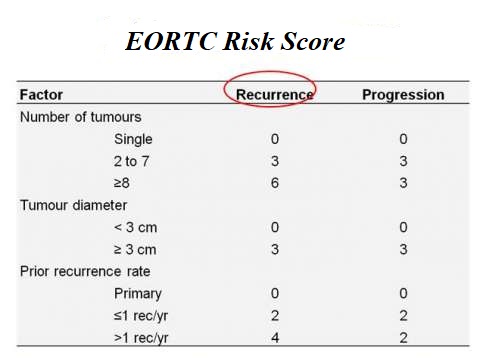
This prognostic calculator is a kind of scoring system based on six clinical and pathological factors:
- number of tumours,
- tumour size (diameter of the largest tumour),
- the previous recurrence rate of cancer,
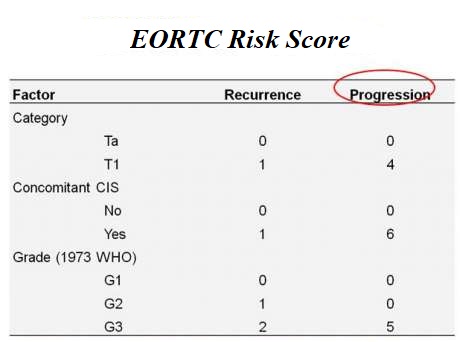
- disease level (T category),
- in situ cancer ( CIS is always high and worsens the prognosis),
- degree of the tumour.
For each of these variables, the patient receives a score from 0 to 6 (both for the risk of recurrence and for progression). This information and data allow us to determine values.
EORTC Risk Scoring Table
Probability of Bladder Occurrence and Progression: At 1 year and 5 years
Risk tables show the state of the disease from 1 to 5 years. Research has shown that the probability of deterioration or recurrence during one year ranges from 15% to 61% and from less than 1% to 17%. After five years, the probability ranges from 31% to 78% and from less than 1% to 45%.
| Recurrence points | Risk of recurrence at 1 year | Risk at 5 years |
| 0 | 15% | 31% |
| 1-4 | 24% | 46% |
| 5-9 | 38% | 62% |
| 10-17 | 61% | 78% |
| Progression points | Risk of progression at 1 year | Risk of progression at 5 years |
| 0 | 0.2% | 0.8% |
| 2-6 | 1% | 6% |
| 7-13 | 5% | 17% |
| 14-23 | 17% | 45% |
Using the data provided to a particular patient, the urologist can discuss the various therapeutic options to determine the most appropriate cure. All these data are very important because they tell about the average group of people covered by the disease the number of people in the population.
The tumour rates are stage-dependent, with five-year recurrence rates of approximately 65% in patients with noninvasive or in situ tumours and 73% in patients with advanced disease at first diagnosis. The overall 5-year survival rate is 77%. However, it all depends on the step of the disease. So, the 5-year survival rate of people with this disease that has not spread beyond the inner layer of the bag wall is 96%.
So, was this post helpful? Meanwhile, read more of our similar articles and suggest to your friends to adopt new knowledge.
Bladder Cancer Recurrence and Progression Calculator – How to Use?
The calculator is used by a person entering the required 6 fragments in the forms explained in the article above. It automatically gives the results of the state of your organism. Very fast and easy.
Bladder Cancer Recurrence and Progression Calculator – Example
Here is one example to see how the to calculate values. The patient enters the first 6 fragments, and our tool calculates the worsening and progression in the interval of 1 to 5 years. It also gives us important information about the organism’s state regarding this disease.
| Number of tumors Single | Tumor diameter < 3 cm |
| Prior recurrence rate primary | Stage of the disease Ta |
| Concomitant CIS No | Tumor grade G1 |
| Recurrence points 0 | Progression points 0 |
| Probability of recurrence at 5 years 31% | Probability of progression at 1 year 0.2% |
| Probability of recurrence at 1 year 15% | Probability of progression at 5 years 0,8% |
FAQ
Are most bladder cancers curable?
A bag tumor can be treated when it is caught early, but it is harder to get rid of when it is detected later.
Does bladder cancer spread fast?
The degree of cancer means how fast cancer can grow. There are two types:
low grade – tumour cells usually grow slowly; most tumors are low grade
high grade –tumour cells look very abnormal and grow quickly. As a result, it is more likely to spread. Almost all muscle-invasive cancers are high grade.
Does the size of bladder tumor matter?
In this type of tumor, the size is very important because, in this way, it is possible to determine which type of cure will be applied and how to suppress its recurrence.
Larger tumor size is associated with prolonged stay, reoperation, readmission, and death.
What’s the prognosis for bladder cancer?
The prognosis is the doctor’s opinion on how likely the disease is to spread and the chances of improvement. Also, the prognosis depends on the type and stage of the tumor, age, and general health.
This disease can usually be effectively treated if it is found before it spreads.
What does high grade mean in bladder cancer?
A high degree means that – tumor cells look abnormal and grow quickly. Therefore, it is more likely to spread. Almost all invasive muscle cancers are high grade.
Can you live without a bladder?
Yes. If your bag has been removed, you will need to get used to the new way of excreting urine from your body. The surgery is called a cystectomy and leaves a change for a lifetime. You may need to bathe differently and adjust your travel habits. This can affect the image of your body.
What are the signs of bladder cancer?
– Blood in urine
– Need for frequent urination
– Pain or burning when urinating
– Inability to urinate when needed
How to prevent bladder cancer recurrence?
Most evidence shows that a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, which contain compounds that protect against cancer, is the best way to avoid its recurrence.
